Multiple Dashboards
It's common to encounter the need for multiple dashboards in the same web application. For example, you may have a dashboard for the system's administrators, and another dashboard for the customers. The diagram below provides a bird's eye view of the Multiple Dashboards concept as implemented by Modular:
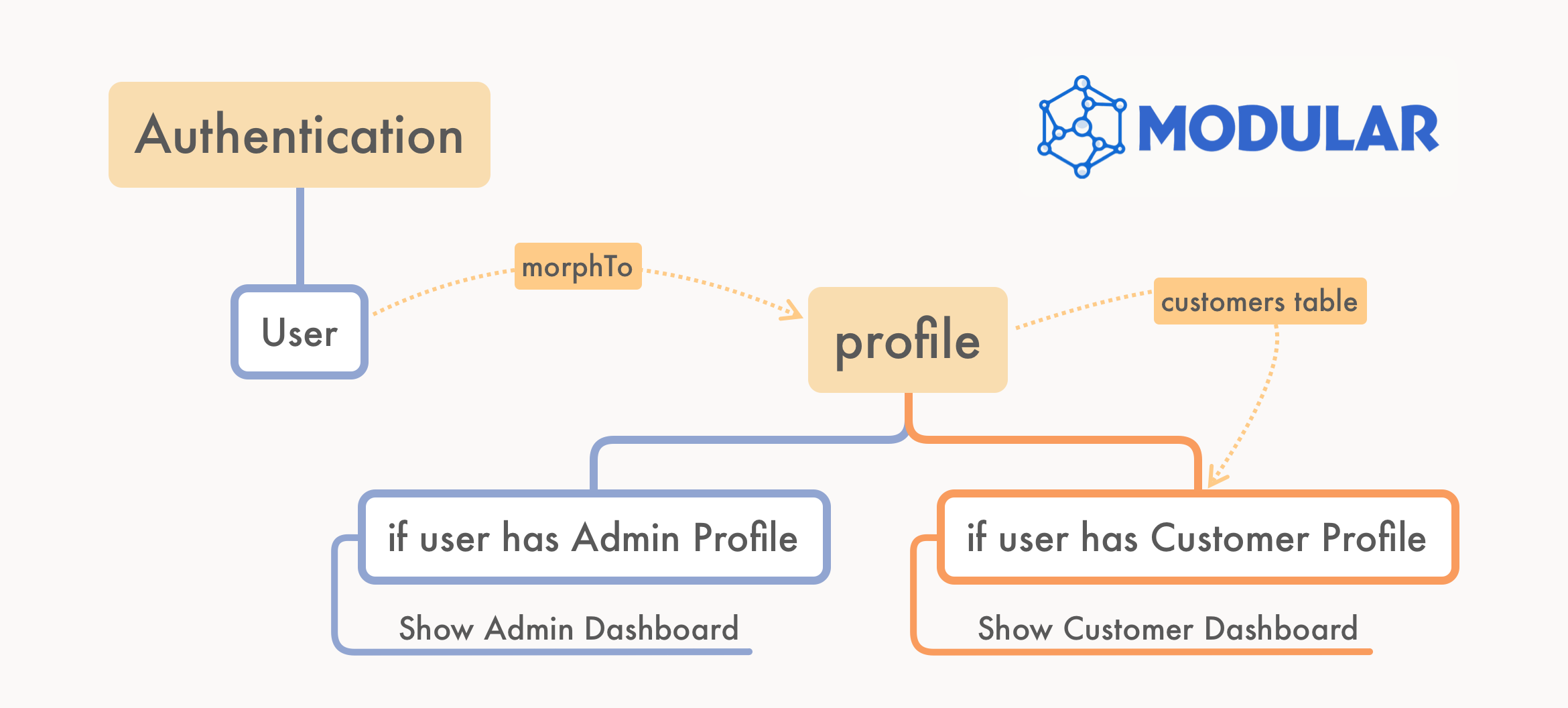
It all starts with profiles
The first step to adopt this Multiple Dashboards concept is to map the different types of users that will access your application. For example, if you have two types of users: user and customer, in the Modules\Support\SupportServiceProvider file, you should explicitly tell Modular to expect these two types of users:
//modules/Support/SupportServiceProvider.php
<?php
namespace Modules\Support;
use Modules\Support\BaseServiceProvider;
class SupportServiceProvider extends BaseServiceProvider
{
public function boot()
{
Relation::morphMap([
'user' => 'Modules\User\Models\User',
'customer' => 'Modules\Customer\Models\Customer',
]);
parent::boot();
}
}Out of the box, creating regular users in Modular will set them with the user profile. If you check your users table, you will see that the profile_type column is set to user and the profile_id will be the same as the user id in context.
But after creating a new customer in your customers table, you will have access to its id. Knowing this, you can create the customer's user setting the profile_type to customer and the profile_id to the id of the customer in context. To do this, you can use multiple approaches as mentioned below.
Using a Model Observer to create the customer user
If your users are being created by admins of the system: in the customer form, you can have the email and password fields together with the fields required by the customer model. After the customer is created, you can create the customer's user automatically, using a Model Observer (for the Customer Model) with the created event listener method (so "Customer created", triggers "User create"). You can use the same approach to define the customer's user ACL roles and permissions (User of profile_type = customer created, triggers the sync of the user with the required ACL Role).
Manually creating the customer user
In some cases, you will need to validate some user information before granting access to the system. Or perhaps the customers are coming from third-party systems through an API integration, and the email and password information are not available. In this scenario, you can create the customer user manually, after the customer is created. In the page that lists the customers, you can have a button to create the user for the customer in context. In this case, just pass the profile_type and profile_id to the create method of Modular's User Module:
<AppButton
class="btn btn-primary"
@click="
$inertia.visit(
route('user.create', {
profile_type: 'customer',
profile_id: customer.id
})
)
"
>
Create User
</AppButton>TIP
You can find more about the Modular ACL (Access Control List) in the ACL Documentation Section .